Upgrade Nginx 1.18 to Nginx 1.26 (Official Nginx Repository)
To upgrade Nginx 1.18 to Nginx 1.26 on Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish), you need to install it from the official Nginx repository instead of the default Ubuntu repository (which contains outdated versions). Here’s the step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Remove Old Nginx Version
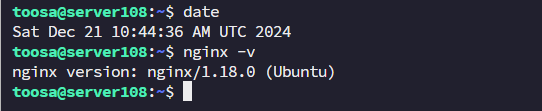
First, check your current installed Nginx version:
nginx -v
If it’s 1.18, remove it to prevent conflicts:
sudo apt remove nginx nginx-core nginx-common -y
sudo apt autoremove -y
Step 2: Add the Official Nginx Repository
Since the Ubuntu repository only provides older versions, add the official Nginx repository.
- Import the Nginx GPG key:
curl -fsSL https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/null
- Add the official Nginx repository:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy nginx" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Step 3: Update Package List and Install Latest Nginx
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx -yJika terjadi error seperti ini:
# sudo apt update
Get:1 http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy InRelease [3,581 B]
Err:1 http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy InRelease
The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY ABF5BD827BD9BF62
Hit:2 http://id.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Get:3 http://id.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease [128 kB]
Hit:4 http://id.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease
Get:5 http://id.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease [129 kB]
Reading package lists... Done
W: GPG error: http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy InRelease: The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY ABF5BD827BD9BF62
E: The repository 'http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy InRelease' is not signed.
N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.Pesan kesalahan tersebut muncul karena kunci GPG untuk repository NGINX belum tersedia di sistem Anda, sehingga apt tidak dapat memverifikasi keaslian paket dari repository tersebut.
Berikut adalah cara untuk menambahkan kunci publik yang hilang (ABF5BD827BD9BF62) dan memperbaiki masalah ini:
Hapus repository yang lama jika ada:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.listTambahkan ulang repository NGINX dengan metode signed-by:
# Unduh kunci dan simpan dengan benar
curl -fsSL https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/nullTambahkan repository NGINX dengan opsi signed-by:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy nginx" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.listPerbarui indeks paket:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx -yStep 4: Verify Nginx Installation
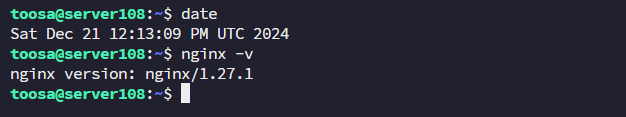
Check the installed version:
nginx -v
It should now show 1.27.0 or the latest stable version.
Step 5: Restart and Enable Nginx
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
(Optional) Step 6: Verify Nginx is Running
Check if Nginx is running:
sudo systemctl status nginx
Check if it’s listening on port 80:
sudo ss -tulnp | grep nginx
Done !
But if You saw some thing like
W: GPG error: http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy InRelease: The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY ABF5BD827BD9BF62It looks like the GPG key for the official Nginx repository is missing or not properly added. Let’s fix this step-by-step.
Step 1: Remove the Old Key (If Exists)
sudo rm -f /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg
Step 2: Import the Correct GPG Key
Now, add the correct Nginx GPG key:
curl -fsSL https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/null
Verify that the key has been added:
gpg --show-keys /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg
It should display something like:
pub rsa4096 2011-08-19 [SC]
ABF5 BD82 7BD9 BF62
Step 3: Correct the Nginx Repository Configuration
Now, re-add the Nginx repository, ensuring it references the signed key correctly:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu jammy nginx" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Step 4: Update and Install Nginx
Try updating your package list again:
sudo apt update
If no errors appear, proceed with installing Nginx:
sudo apt install nginx -y
Step 5: Verify the Installation
Check the installed Nginx version:
nginx -v
If it shows 1.27, the upgrade was successful. 🎉
Troubleshooting
If you still get a NO_PUBKEY error, try manually adding the key:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys ABF5BD827BD9BF62
Then update again:
sudo apt update
That should fix the issue.